Recent publication - 11/2022
- Detection of Homologous Recombination Intermediates via Proximity Ligation and Quantitative PCR in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Diedre Reitz, Jérôme Savocco Aurèle Piazza, Wolf-Dietrich Heyer (Sept. 2022), Journal of vizualized experiments.
We published a method paper together with the lab of Wolf Heyer, which will soon be shot as a video, at the Journal of Video Experiments. The goal is to facilitate the adoption of proximity ligation-based methodologies to the study of DNA recombination by the relevant communities.
Paper: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36155960/
-
Myotonic dystrophy RNA toxicity alters morphology, adhesion and migration of mouse and human astrocytes. Dincã DM, Lallemant L, González-Barriga A, Cresto N, Bra, SO, Sicot G, Pillet L, Polvèche H, Magneron P, Huguet-Lachon A, Benyamine H, Azotla-Vilchis CN, Agonizantes-Juárez LE, Tahraoui-Bories J, Martinat C, Hernández-Hernández O, Auboeuf D, Rouach N, Bourgeois CF, Gourdon G and Gomes-Pereira M. 2022. Nat Commun, 13(1):3841.
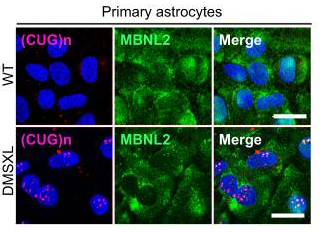
This paper results from a fruitful collaboration between the Centre de Recherche en Myologie, the Collège de France (Paris), the AFM-Téléthon flagship institute I-Stem (Evry) and the ReGArDS team at LBMC. Using a mouse model of myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1), a prototypic toxic RNA disorder resulting in multiple muscular and neurological alterations, this study demonstrates that DM1 astrocytes exhibit impaired ramification and polarization in vivo and defects in adhesion, spreading, and migration. This is in line with splicing defects that are more severe than in neurons and that affect primarily transcripts that regulate cell adhesion, cytoskeleton, and morphogenesis.
Paper : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35789154/
- RNA helicase-dependent gene looping impacts messenger RNA processing. Sophie Terrone, Jessica Valat, Nicolas Fontrodona , Guillaume Giraud, Jean-Baptiste Claude, Emmanuel Combe, Audrey Lapendry, Hélène Polvèche, Lamya Ben Ameur , Arnaud Duvermy, Laurent Modolo, Pascal Bernard, Franck Mortreux , Didier Auboeuf, Cyril F Bourgeois ( Sept. 2022), Nucleic Acids Res. 50(16):9226-46.
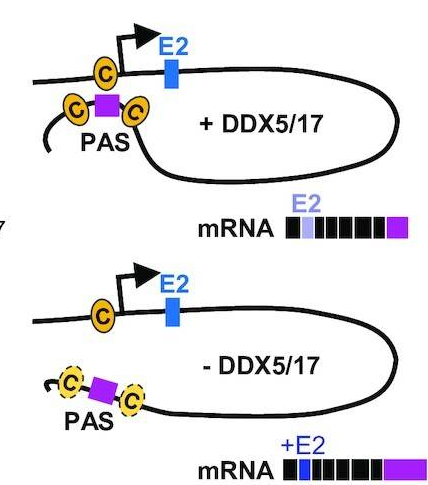
In this paper, the ReGArDS team shows that chromatin loops regulated by RNA helicases DDX5 and DDX17 spatially connect the helicase-targeted exons with their promoter, and we provide the first direct evidence that de novo gene looping modifies alternative splicing and polyadenylation of pre-messenger RNAs. We propose that RNA helicases promote transcription across DNA and/or RNA structured regions, which contributes to the processing of internal and terminal exons.
Paper: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36039747/
- Prognostic impact of ABCA3 expression in adult and pediatric acute myeloid leukemia: an ALFA-ELAM02 joint study. Ceraulo A, Lapillonne H, Cheok MH, Preudhomme C, Dombret H, Terré C, Lambert J, Leverger G, Bertrand Y, Mortreux F and Wattel E (2022). Blood Adv. 6(9):2773-2777.
This article presents the results of Antony Ceraulo's thesis co-directed by Franck Mortreux (ReGArDS team) and Eric Wattel (Hôpital Lyon Sud). The data show that ABCA3 expression is an independent prognostic factor in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and helps to predict response to gemtuzumab-ozogamycin in adult AML, thereby improving the risk stratification of AML patients.
Paper : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35008099/
- The endogenous HBZ interactome in ATL leukemic cells reveals an unprecedented complexity of host interacting partners involved in RNA splicing. Shallak M, Alberio T, Fasano M, Monti M, Iacobucci I, Ladet J, Mortreux F, Accolla RS, Forlani G. (2022). Front Immunol. 13:939863.
This study follows previous work of the ReGArDS team on the role of DDX17 helicase in mediating the effects of the viral oncoprotein TAX on alternative splicing during HTLV-1 infection (Ameur LB et al., Nat. Com., 2020). Here, Franck Mortreux and Julien Ladet, in collaboration with Roberto Accolla's team (University of Insubria, Varese, Italy), show that the other viral oncogene HBZ also interacts with DDX5 and DDX17, as well as with other splicing factors such as U2AF1, U2AF2, SRSF1 and HNRNPC, and that they affect splicing regulation in human lymphocytes. These results propose HBZ as a crucial player in a complex series of events leading to splicing changes during HTLV-1-related leukemogenesis.
Paper : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35979358/
-
Altered splicing of ATG16-L1 mediates acquired resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors of EGFR by blocking autophagy in non-small cell lung cancer. Hatat A, Benoit-Pilven C, Pucciarelli A, de Fraipont,F, Lamothe L, Perron P, Rey A, Levra MG, Toffart A, Auboeuf D, Eymin B and Gazzeri, S (2022). Mol Oncol. 16(19):3490-3508
paper : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35593080/
- Dynamical modeling of the H3K27 epigenetic landscape in mouse embryonic stem cells. Kapil Newar, Amith Z Abdulla, Hossein Salari, Eric Fanchon, Daniel Jost (2022) PLoS Comp Biol, 18: e1010450.
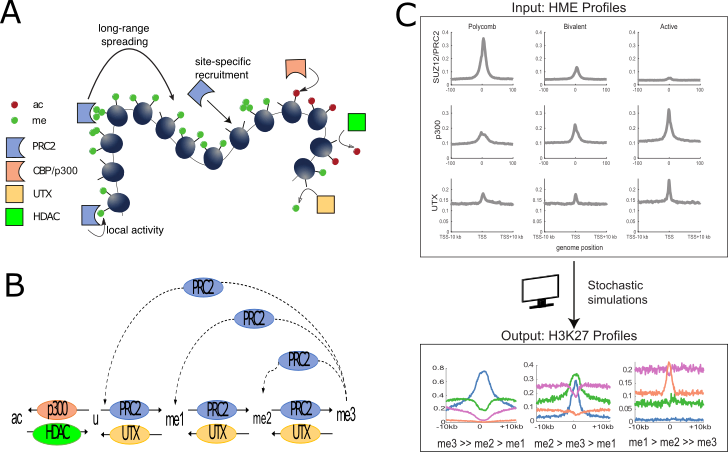
The Polycomb system via the H3K27me3 mark plays central roles in the silencing of many lineage-specific genes during development. Experiments suggest that the recruitment of histone modifying enzymes (PRC2) at specific sites and their spreading capacities from these sites are key to the regulation of Polycomb-target genes. Here, we tested whether such mechanisms, as a minimal set of qualitative rules, are quantitatively compatible with data, using mathematical modeling. Within the biological context of mouse embryonic stem cells, our model showed quantitative agreement with experimental profiles of H3K27 modifications and with their measured dynamics. We demonstrated the key role of the reader-writer module of PRC2 and of the competition between the binding of activating and repressing enzymes in shaping the H3K27 landscape around transcriptional start sites.
Paper : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36054209/
-
Painters in chromatin: a unified quantitative framework to systematically characterize epigenome regulation and memory. Amith Z Abdulla, Cédric Vaillant, Daniel Jost (2022) Nucleic Acids Res, 50: 9083-9104.
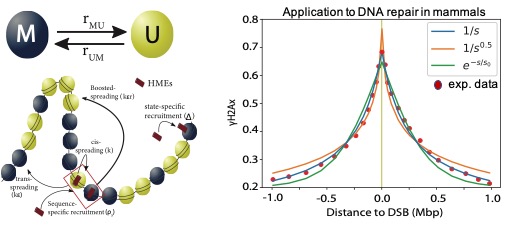
Many epigenetic regulatory mechanisms rely on the molecular cooperativity of ‘reader–writer’ enzymes. In this work, we focus on the fundamental processes behind the epigenome memory encoded by post-translational modifications of histone tails. Based on experimental knowledge, we introduce a unified modeling framework, the painter model, describing the mechanistic interplay between sequence-specific recruitment of chromatin regulators, chromatin-state-specific reader–writer processes and long-range spreading mechanisms. A systematic analysis of the model building blocks highlights the crucial impact of the 3D genome on the stability of epigenomic domains. We applied our framework to analyze diverse experimental data, from the propagation of γH2AX around DNA breaks in human cells to the maintenance of heterochromatin in fission yeast.
Paper : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36018799/
