The eWAN objective is to allow the users to test their own applications or protocols on an emulated grid before the test or deployments on a real grid environment.
The researcher has three possibilities to test his work:
- Real grid environments: Too susceptible to real aleatory conditions, not easy to control and difficult to get a good grid account.
- Simulation option: On the other hand we have the simulation option. On simulations the scalability are maximal, but the performance of each simulated node (router, client, link) falls down by the execution of several nodes on one physical machine.
- Emulation option: The emulation doesn't scale like the simulation, since one portion is simulated and the rest is real. On each physical machine only one node is assigned, without performance limits or loss. It's an intermediate version.
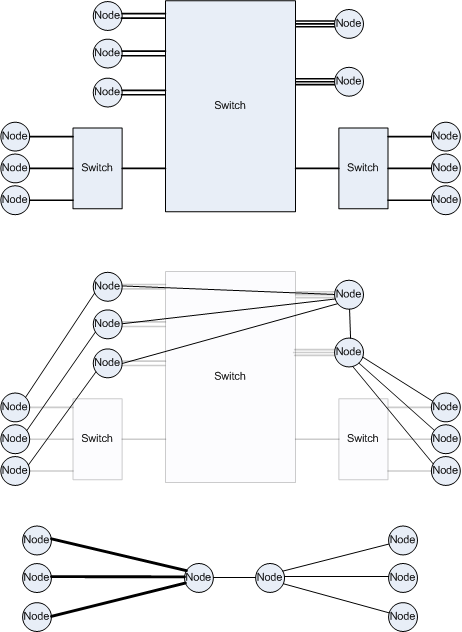
EWAN is an emulator. It is deployed on a cluster, assigning each topology node to deploy to a physical node. The topological links to emulate are assigned to other machines, with a maximum of two links (in the case of the two links which connect two nodes -a link and its inversed-) for each machine.
Figure 1:
Transform your cluster into a grid
|
 |
This document offers detailed explanations over eWAN, the manner in which it works and the different ways in which you can use it. It describes the configuration options and also gives utilisation examples in order to help you to work with eWAN.
Subsections
sansol
2006-06-09