Yuting Zeng
Quantitative UV-visible Investigation of Vanadium Dispersion in Al or Ti modified MCM-41Silicas
Yuting Zheng
Transition metal ions supported on mesostructured porous silicas such as Ti-MCM-41 attract a lot of attention because of their remarkable performance in catalytic oxidation of hydrocarbons. The vanadium equivalent is potentially interesting since this metal allows direct oxidation of alkanes into primary alcohols, a highly relevant reaction for industry. Unfortunately, V5+ or V4+ ions tend to leach out polluting the products and leading to drastic drop of catalytic activity. In this work, vanadyl sulfate solution is incorporated by wetness impregnation in MCM-41 silicas the surface of which have modified by grafting Al or Ti alkoxides. These ions are known to improve the anchoring of vanadyl ions and also to favors the dispersion of vanadium on the surface. The originality of our approach lies on the quantitative treatment of the Diffuse Reflectance (DR) UV-visible spectra of the calcined samples according to a previous study on V5+ supported on non porous fumed SiO2.
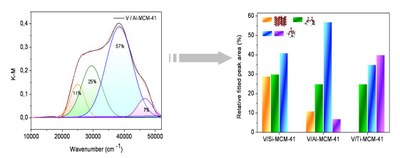
Figure 1 : DR UV-visible data: on the left, typical spectrum with a Gaussian deconvolution as proposed in ref. 1; on the right, bar diagrams providing the percentage of species corresponding to each kind of vanadium species supported on silica pure (left), Al modified (middle) and Ti modified (right) MCM-41: orange, green, blue and violet stand for large V205 aggregates, small oxide clusters of V5+ ions, hydrated (penta or hexa coordinated ) isolated species and tetrahedral isolated V5+ ions.
The preliminary DR UV-visible study evidences a clear blue shift of the absorption spectra in the calcined catalysts in the presence of Al3+ and even more on the presence of Ti4+ ions. The bands are assigned to a mixture of clustered or isolated V fitted by a single Gaussian curve and also more or less hydrated isolated species (Fig. 1, left). The concentration of the isolated species drastically increases when Ti or in lesser extent when Al ions are present on the MCM-41 silica surface (Fig. 1, right). This is consistent with a stronger covalent Ti-O-V than Al-O-V or Si-O-V µ-oxo bridges. The vanadium leaching tests show consistently a better retention of vanadium in the presence Al or Ti. Other techniques like electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) are also used to get better insights on vanadium dispersion. Some molecular engineering of the silica surface is at work to improve the metal dispersion and its affinity to the surface and catalytic tests on oxidation reaction of alkanes are planned.