Bio-capteurs à base de complexes xenon-cryptophane .
Les développements récents de fonctionnaliser cryptophanes stimulé le développement de nouvelles molécules pour l'encapsulation de xénon pour l'imagerie biomédicale par RMN. Hyperpolarisé 129 Xe RMN permet de détecter à faible concentration des analytes au moyen d'un biocapteur de xénon qui consiste en une soluble dans l'eau cryptophane-A qui encapsule le xénon. En collaboration avec le groupe de A. Pines (Berkeley), nous avons utilisé un biotinylé xénon cryptophane complexe à évaluer les différents paramètres (changement de conformation, xénon échange, etc) qui interfèrent quand l'interaction avec les biocapteurs une protéine cible (ChemBioChem, 2006) .
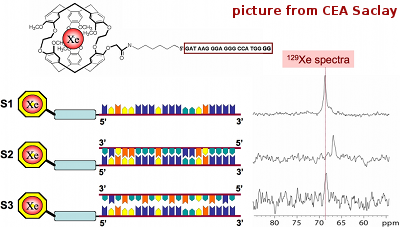
Un cryptophane faite d'un brin de nucléotides greffés sur un fragment de cryptophane-A a été synthétisé pour la détection de cibles spécifiques de nucléotides. Le capteur bio-ainsi obtenue a été capable de se lier au xénon qui a été capable de détecter le nucléotide complémentaire dans la gamme micromolaire en utilisant la spectroscopie laser polarisé 129Xe RMN. Ce travail a été mené en collaboration avec le laboratoire de RMN au CEA Saclay et avec le laboratoire bioMérieux-CNRS à l'ENS-Lyon (ChemPhysChem, 2007).