S. Gautier
| When |
Feb 12, 2015 à 01:30 PM |
|---|---|
| Where |
Grande Salle cbp |
| Contact |
C. Michel |
Catalytic reactivity at high coverage, a theoretical approach: butadiene hydrogenation on Pt(111) and Sn/Pt(111)
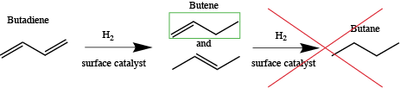
The selective hydrogenation of butadiene into butene is of great interest for the butene purification process. Platinum and tin-platinum surface alloy are known to be among the best metal catalysts for this application. The reactivity of butadiene on Pt(111) surface and Pt/Sn-Pt(111) surface alloy was already studied by our group at low coverage of hydrogen[1,2] within the periodic DFT framework using the VASP package. However, the reaction is done under a pressure of H2 of 1 bar and at a temperature of 300 K. In this study, our aim is to take into account the effect of those two factors. For that purpose, a thermodynamic model was coupled to the DFT calculations. This allowed understanding the behaviour and relative stability of the different species adsorbed on the surface with regard to their coverage at 300 K and 1 bar of H2. In a parallel work, we tested several relatively new functionals, which were made to better describe the long-range interactions. We showed that the adsorption of several unsaturated molecules was accurately described when using these Van der Waals functionals, by comparing our results to micro calorimetric experimental data obtain by Campbell et al [3,4]. We established that the reactivity of butadiene is strongly coverage dependent, on Pt(111) and on Pt/Sn-Pt(111). Passing from low to high coverage, the adsorption conformation of butadiene changes, including its coordination to the surface. Even more interestingly, the reaction mechanism is affected and changes from Langmuir-Hinshelwood at low coverage, to Eley-Rideal mechanism at high coverage. The latter mechanism implies a reaction between adsorbed hydrogen and physisorbed butadiene, which makes the dispersion forces essential for this mechanism. This confirmed the need of using Van der Waals functionals for this study.
References
1 A. Valcarcel, A. Clotet, J.M. Ricart, F. Delbecq and P. Sautet, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109, 14175.
2 F. Vigné, J. Haubrich, D. Loffreda, P. Sautet and F. Delbecq, J. Catal., 2010, 275, 129.
3 S.Gautier, P. Fleurat-Lessard, S. Steinmann, C. Michel and P. Sautet. To be submitted.
4 C. Campbell et al, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2008, 37, 2172.