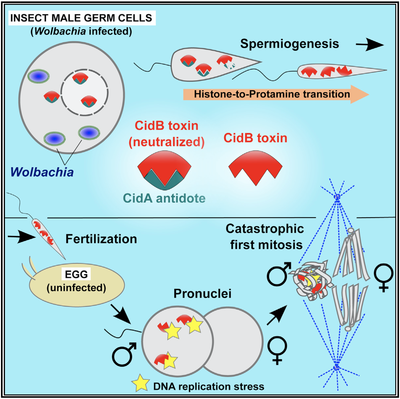
Wolbachia Toxin-Antidote systems and sperm poisoning
Wolbachia are endosymbiotic bacteria that infect many insect orders as well as other arthropods. They have evolved sophisticated mechanism to control the sexual reproduction of their hosts. We study Cytoplasmic Incompatibility, a sterility syndrome caused by Wolbachia in which sperm from infected males kill eggs from uninfected females. In particular, we are studying a pair of Wolbachia proteins (CifB and CifA) that form a transgenerational Toxin-Antidote system.
Contact: Béatrice Horard and Benjamin Loppin
Our recent Current Biology article: "Paternal transmission of the Wolbachia CidB toxin underlies cytoplasmic incompatibility" by Horard et al. is now featured on the CNRS INSB portal: "https://www.insb.cnrs.fr/fr/cnrsinfo/wolbachia-manipule-les-spermatozoides-dinsectes-grace-une-toxine-nucleaire"